Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-065, 379 Pages, 1999/10
A database for diffusivity for a data setting of effective diffusion coefficients in rock matrices in the second progress report, was developed. In this database, 3 kinds of diffusion coefficients: effective diffusion coefficient (De), apparent diffusion coefficient (Da) and free water diffusion coefficient (Do) were treated. The database, based on literatures published between 1980 and 1998, was developed considering the following points. (1)Since Japanese geological environment is focused in the second progress report, data for diffusion are collected focused on Japanese major rocks. (2)Although 22 elements are considered to be important in performance assessment for geological disposal, all elements and aquatic tracers are treated in this database development considering general purpose. (3)Since limestone, which belongs to sedimentary rock, can become one of the natural resources and is inappropriate as a host rock, it is omitted in this database development. Rock was categorized into 4 kinds of rocks; acid crystalline rock, alkaline crystalline rock, scdimentaly rock (argillaceous/tuffaceous rock) and sedimentary rock (psammitic rock/sandy stone) from the viewpoint of geology and mass transport. In addition, rocks around neutrality among crystalline rock were categorized into the alkaline crystalline rock in this database. The database is composed of sub-databases for 4 kinds of rocks. Furthermore, the sub-databases for 4 kinds of the rocks are composed of databases to individual elements, in which totally, 24 items such as species, rock name, diffusion coefficients (De, Da, Do), obtained conditions (method, porewater, pH, Eh, temperature, atmosphere, etc.), etc. are input. As a result of literature survey, for De values for acid crystalline rock, totally, 207 data for 18 elements and one tracer (hydrocarbon) have been reported and all data were for granitic rocks such as granite, granodiorite and biotitic granite. For alkaline crystallinc rock, ...
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8400 99-062, 16 Pages, 1999/10
Effective diffusion coefficients (De) for Ni , Sm
, Sm , Am
, Am and SeO
and SeO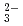 were measured as a function of the ionic charge of diffusion species to quantitatively evaluate the effect of ionic charge in compacted bentonite. The De measurements for Ni
were measured as a function of the ionic charge of diffusion species to quantitatively evaluate the effect of ionic charge in compacted bentonite. The De measurements for Ni and Sm
and Sm were carried out for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg
were carried out for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with a simulated porewater condition of pH5
with a simulated porewater condition of pH5 6 by through-diffusion method. The De values for SeO
6 by through-diffusion method. The De values for SeO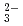 were measured for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg
were measured for a bentonite dry density of 1.8 Mg m
m with a simulated porewater condition of pH11. The De measurements for Am
with a simulated porewater condition of pH11. The De measurements for Am were carried out for the dry densities of 0.8, 1.4 and l.8 Mg
were carried out for the dry densities of 0.8, 1.4 and l.8 Mg m
m with a porewater condition of pH2 in order to check cation exclusion. Sodium bentonite, Kunigel-V1 was used for those measurements. For the measurements of Am, H-typed Kunigel-V1 which interlayer ion (Na
with a porewater condition of pH2 in order to check cation exclusion. Sodium bentonite, Kunigel-V1 was used for those measurements. For the measurements of Am, H-typed Kunigel-V1 which interlayer ion (Na ) was exchanged with H
) was exchanged with H was used, because the experiments are carried out for a low pH range. The order of obtained De values was Sm
was used, because the experiments are carried out for a low pH range. The order of obtained De values was Sm
 Ni
Ni
 Am
Am
 SeO
SeO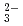 . These De values were compared to those reported to date. Consequently, the order of De values was Cs
. These De values were compared to those reported to date. Consequently, the order of De values was Cs
 Sm
Sm
 HTO
HTO  Ni
Ni
 anions (I
anions (I , Cl
, Cl , CO
, CO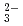 , SeO
, SeO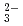 TcO
TcO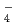 , NpO
, NpO CO
CO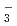 , UO
, UO (CO
(CO )
)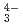 ), showing a tendency of cations
), showing a tendency of cations  HTO
HTO  anions. Only the De values of Am
anions. Only the De values of Am were approximately the same degree as those of anions. The reason that the De of Ni
were approximately the same degree as those of anions. The reason that the De of Ni was lower than that of HTO may be because the free water diffusion coefficient (Do) of Ni
was lower than that of HTO may be because the free water diffusion coefficient (Do) of Ni is about 1/3 of that of HTO. The cause that the De of Am
is about 1/3 of that of HTO. The cause that the De of Am was approximately the same degee as those of anions may be because the Do of Am
was approximately the same degee as those of anions may be because the Do of Am is about 1/3 of that of HTO and that Am
is about 1/3 of that of HTO and that Am was electrostatically repulsed from the surface of bentonite by cation exclusion. The formation factors (FF), calculated normalizing Do, were in the ...
was electrostatically repulsed from the surface of bentonite by cation exclusion. The formation factors (FF), calculated normalizing Do, were in the ...
Sato, Haruo; ; ; *; *; Yui, Mikazu
PNC TN8410 97-127, 57 Pages, 1997/08
Retardation of key nuclides is one of the most important mechanisms to be examined specifically and modelled for the performance assessment of geological disposal of radioactive waste. We have been studing diffusion of nuclides into the pore spaces of the rock matrix, sorption of nuclides on the rock pore surfaces and pore properties to quantify the degree of nuclide retardation in fractured crystalline rock. The work has concentrated on predominant water conducting fracture system in the host granodiorite in the Kamaishi In Situ Test Site, which consists of fracture fillings and altered granodiorite. Through-diffusion experiements to obtain effective and apparent diffusion coefficients (Da and De, respectively) for Na, Cs, HTO, Cl and Se as a function of ionic charge at 22  25
25 C and batch sorption experiments for Cs, Sr, Se,
C and batch sorption experiments for Cs, Sr, Se,  U and
U and  Pu were conducted on fracture fillings, altered and intact granodiorite. The experiments only for Se, a redox sensitive element, were done in an N2-atmospheric glove box (O
Pu were conducted on fracture fillings, altered and intact granodiorite. The experiments only for Se, a redox sensitive element, were done in an N2-atmospheric glove box (O
 1 ppm) to keep the chemical species. In situ groundwater (pH8.7
1 ppm) to keep the chemical species. In situ groundwater (pH8.7 9.5) sampled from the same place as rock samples was used for the experiments. Porosity and density of cach rock sample were determined by both water saturation method and mercury porosimetry, and pore-size distribution and specific surface area of pores were measured by mercury porosimetry. The porosity is in the order; fracture fillings (5.6%)
9.5) sampled from the same place as rock samples was used for the experiments. Porosity and density of cach rock sample were determined by both water saturation method and mercury porosimetry, and pore-size distribution and specific surface area of pores were measured by mercury porosimetry. The porosity is in the order; fracture fillings (5.6%)  altered rock (3.2%)
altered rock (3.2%)  intact rock (2.3%). The pore-size distribution of the intact and altered granodiorite is ranging from 10 nm to 0.2 mm, and the fracture fillings have that of 50 nm to 0.2 mm, but a lot of pores were found around 100 nm and 0.2 mm in the fracture fillings. The effective diffusion coefficients for all species (Na
intact rock (2.3%). The pore-size distribution of the intact and altered granodiorite is ranging from 10 nm to 0.2 mm, and the fracture fillings have that of 50 nm to 0.2 mm, but a lot of pores were found around 100 nm and 0.2 mm in the fracture fillings. The effective diffusion coefficients for all species (Na , Cs
, Cs , HTO, Cl
, HTO, Cl , Se0
, Se0
 ) are in the order of fracture fillings
) are in the order of fracture fillings  altered rock
altered rock  intact rock in proportion to these porosities. Effective diffusion ...
intact rock in proportion to these porosities. Effective diffusion ...
; ; ;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 174(1-2), p.201 - 208, 1980/00
no abstracts in English